What are the regular voluntary prayers?
The regular voluntary prayers (known in Arabic as rawātib, and colloquially as 'Sunnah prayers') are optional but highly recommended prayers that were performed by the Prophet Muhammad (may the peace and blessings of Allah be upon him).
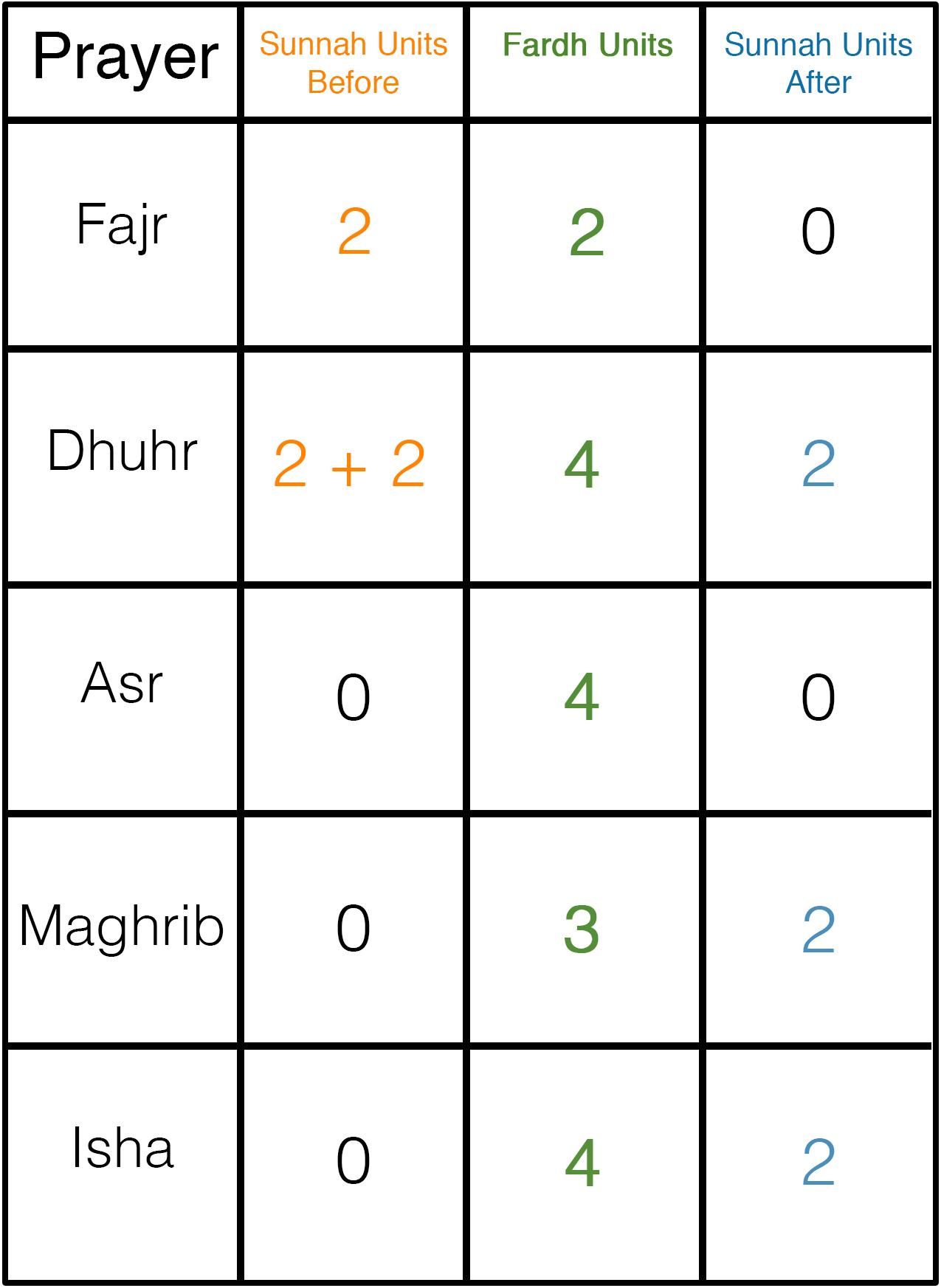
The format is as follows:
- Two rak'ah (units of prayer) before the Fajr prayer.
- Two sets of two rak'ah before the Dhuhr prayer (four in total).
- Two rak'ah after the Dhuhr prayer.
- Two rak'ah after the Maghrib prayer.
- Two rak'ah after the 'Ishā' prayer.
This is because of the following narration from the Prophet Muhammad (may the peace and blessings of Allah be upon him):
"Whoever prays twelve rak'ah during the night and day, a house will be built for him in Paradise: four before Dhuhr and two after, two rak'ah after Maghrib, two rak'ahs after 'Ishā' and two rak’ah before Fajr prayer." [an-Nasā'ī: 1794]
It is also important to note that the two units of prayer before Fajr, along with the witr prayer hold a special importance, in that the Prophet (may the peace and blessings of Allah be upon him) would not miss them, even when he was sick or travelling. Therefore, those two should be given a higher importance and should not be missed, except on very rare occaisions.
When is the correct time to pray the regular voluntary prayers?
There are two types of regular voluntary prayers: those that come before a compulsory prayer, and those that come after.
As for those voluntary prayers which come before, their time begins from the beginning of the prayer time (usually signified by the adhaan - the call to prayer), until the time of the iqaamah (i.e., until the compulsory prayer begins).
As for those voluntary prayers which come after, their time is from the end of the compulsory prayer, until the time for that prayer ends.